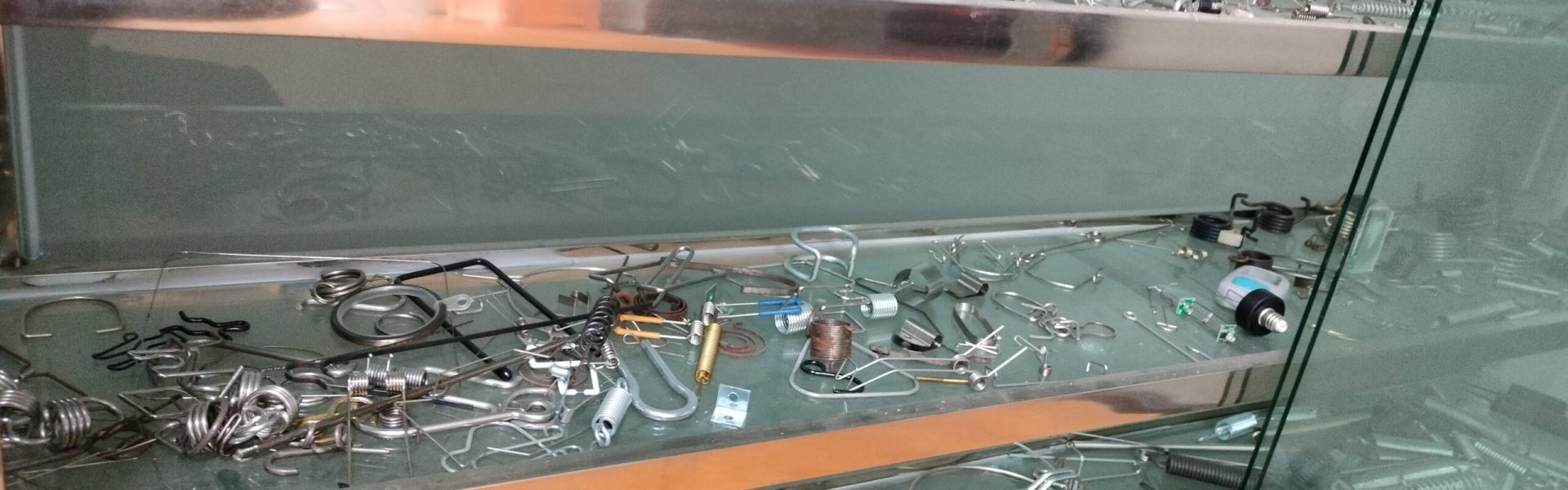





Our springs are crafted to meet exact specifications, ensuring superior performance and reliability.

From stainless steel to specialized alloys, we work with a variety of materials to meet your requirements.

Whether you need compression springs, torsion springs, extension springs, or wire forms, we deliver custom solutions.

Direct factory pricing ensures you get the best value for top-tier quality.

Streamlined processes allow us to deliver your orders on time, every time.

We efficiently handle international logistics to deliver anywhere in the world.



Springs are the unsung heroes in many industries, providing the flexibility, strength, and precision needed for countless applications. Whether you’re designing high-performance machinery or everyday tools, selecting the right material ensures reliability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Let’s break down the essentials to help you make an informed decision!
Spring steels are incredibly popular due to their combination of elasticity, tensile strength, and fatigue resistance. They’re ideal for applications where springs are under constant stress or load.
If your application involves exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme weather, stainless steel is your go-to material. These alloys are resistant to rust and ensure long-lasting performance.
Sometimes, your application calls for something extra. That’s where specialty materials like superalloys and high-strength composites come in.
Case 1: Marine Equipment Manufacturer
A client designing springs for deep-sea applications chose 316L stainless steel for its superior resistance to saltwater corrosion. This decision doubled the service life of their products and reduced maintenance costs by 30%.
Case 2: Heavy Machinery Builder
A manufacturer of industrial presses switched to SWP alloy steel for their tension springs. The result? Springs withstood 20% higher loads and lasted 50% longer under continuous operation.
Case 3: Food Processing Startup
For springs in food slicers, 304 stainless steel was the perfect choice due to its affordability and compliance with food safety standards. The startup saved 15% on costs while ensuring hygienic performance.
| Serial No. | Steel Grade | C (%) | Si (%) | Mn (%) | Cr (%) | Mo (%) | V (%) | B (%) | Ni (%) | Cu (%) | P (%) | S (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 65 | 0.62–0.70 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.50–0.80 | ≤ 0.25 | — | — | — | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 2 | 70 | 0.62–0.75 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.50–0.80 | ≤ 0.25 | — | — | — | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 3 | 85 | 0.72–0.85 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.50–0.80 | ≤ 0.25 | — | — | — | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 4 | 65Mn | 0.62–0.70 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.90–1.20 | ≤ 0.25 | — | — | — | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 5 | 55Si2Mn | 0.52–0.60 | 1.50–2.00 | 0.60–0.90 | ≤ 0.35 | — | — | — | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 6 | 55Si2MnB | 0.52–0.60 | 1.50–2.00 | 0.60–0.90 | ≤ 0.35 | — | — | 0.0005–0.004 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 7 | 55Si2Mn VB | 0.52–0.60 | 0.70–1.00 | 1.00–1.30 | ≤ 0.35 | — | 0.08–0.16 | 0.0005–0.0035 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 8 | 60Si2Mn | 0.56–0.64 | 1.50–2.00 | 0.60–0.90 | ≤ 0.35 | — | — | — | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 9 | 60Si2MnA | 0.56–0.64 | 1.60–2.00 | 0.60–0.90 | ≤ 0.35 | — | — | — | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.030 |
| 10 | 60Si2CrA | 0.56–0.64 | 1.40–1.80 | 0.40–0.70 | 0.70–1.00 | — | — | — | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.030 |
| 11 | 55CrVA | 0.56–0.64 | 1.40–1.80 | 0.40–0.70 | 0.90–1.20 | — | 0.10–0.20 | — | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 12 | 60CrMnA | 0.56–0.64 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.70–1.00 | 0.70–1.00 | — | — | — | 0.25 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 13 | 50CrVA | 0.46–0.54 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.50–0.80 | 0.80–1.10 | — | 0.10–0.20 | — | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 14 | 30CrV2A | 0.26–0.34 | 0.17–0.37 | ≤ 0.40 | 2.00–2.50 | — | 0.50–0.80 | 4.4–5.0 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
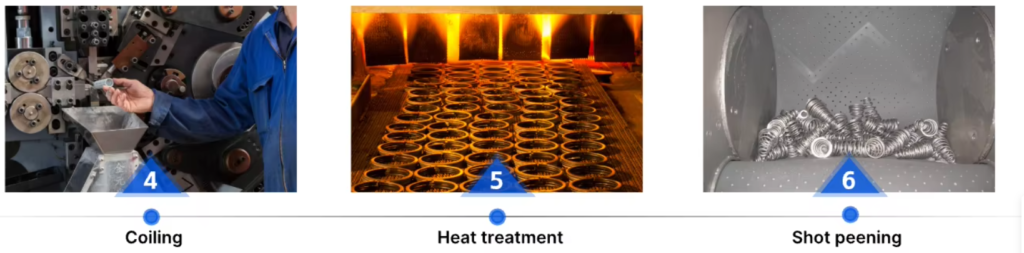
Spring heat treatment is essential for optimizing mechanical properties, ensuring durability, and enhancing fatigue resistance. Various strengthening techniques, such as quenching, tempering, and surface treatments, are applied based on material type and application requirements.
The heat treatment process for springs can be categorized into three types:
The quenching process ensures uniform martensitic transformation, followed by tempering to relieve stress and enhance toughness. Techniques such as isothermal tempering further improve plasticity and toughness, ensuring the spring maintains dimensional accuracy and mechanical stability.
| Process Type | Description | Materials Used | Key Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching & Tempering | Heating above Ac3, holding, then rapid cooling and tempering. | High-carbon steel, alloy steel | Increases strength, hardness, and elasticity. |
| Cold Work Strengthening | Uses mechanical deformation instead of heat treatment. | Stainless steel wire, cold-rolled steel strips | Enhances work-hardening properties. |
| Aging Treatment | Additional heat stabilization after initial processing. | Certain alloy materials | Improves stability and strength. |
| Isothermal Quenching | Maintains temperature above Ms, cools in molten salt. | High-carbon steel, alloy springs | Enhances toughness and plasticity. |
| Controlled Tempering | Gradual cooling to prevent deformation. | Precision springs, mechanical components | Reduces internal stress and ensures accuracy. |
This structured approach ensures that each heat treatment method is aligned with specific material properties and application requirements for optimized performance.
The heat treatment of springs:
| Method | Process Description | Key Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Heat Treatment | Heating and cooling steel to adjust mechanical properties | Increases strength, elasticity, and durability | Medium to high-carbon steel springs |
| Surface Hardening Treatment | Carburizing, nitriding, or induction hardening of the outer layer | Enhances wear resistance while keeping core toughness | Automotive and industrial springs |
| Aging & Tempering | Heat treatment to relieve internal stresses and refine microstructure | Improves stability and mechanical consistency | Precision and high-load springs |
| Steel Grade | Austenitizing Temperature (°C) | Isothermal Quenching Temperature (°C) | Cooling Time (min) | Hardness (HRC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | 820 ± 10 | 320 – 340 | 15 – 20 | 46 – 48 |
| 60Si2MnA | 870 ± 10 | 260 | 20 – 25 | 50 – 52 |
| 50CrVA | 850 ± 10 | 300 | 20 – 25 | 55 – 57 |
| Steel Type | Heat Treatment Process | Hardness (HRC) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Impact Toughness (J/cm²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50CrVA | Conventional Quenching + Tempering | 48 | 1750 | 1500 | 10 | 44 |
| 60Si2MnA | Isothermal Quenching + Tempering | 47 | 1900 | 1750 | 11 | 46 |
| 65Si2MnWA | Isothermal Quenching + Tempering | 50 | 2100 | 1980 | 9 | 43 |
This table format provides a clear and organized comparison of different heat treatment techniques for springs.

Xiamen Linspring was able to manufacture my custom order to specifications and was helpful and communicatie along the way.The quality of the delivered product was good.

This was my second order with Linspring. The seller is great to communicate with and the spring were perfect,just like the first order. Thank you for your prompt,courteous.

Very happy with our custom springs. On time and shipping was fast
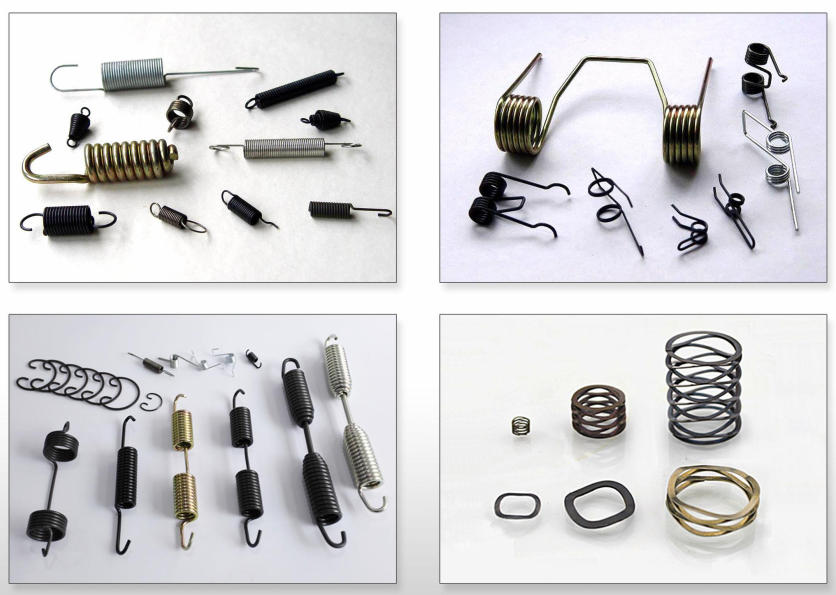



Springs are essential components in countless industries, from automotive and aerospace to medical devices and household appliances. Custom springs, in particular, offer tailored solutions to meet specific requirements for performance, size, material, and application. Designing a custom spring requires careful consideration of numerous factors, from functionality to environmental conditions.
Compression Springs
Tension Springs
Torsion Springs
Flat Springs
Specialty Springs
Choosing the right material is critical for the performance and durability of a custom spring. Some common materials include:
Carbon Steel
Stainless Steel
Alloy Steel
Phosphor Bronze and Beryllium Copper
Titanium
Inconel and Other Superalloys
When designing a custom spring, there are several factors to consider:
Spring Type: Choose the appropriate spring type (compression, tension, etc.) based on the application.
Load Requirements:
Spring Dimensions:
Material Selection: Choose a material that meets the application’s environmental, strength, and durability requirements.
Stress and Fatigue:
Operating Environment:
End Type:
Manufacturing Constraints:
Define Your Requirements:
Choose a Material:
Work with LINSPRING:
Prototype Development:
Final Production:
Provide Clear Specifications:
Request Samples:
Discuss Compliance:
Leverage Expertise:
Plan for Scalability:
Custom springs are a game-changer for applications that demand precision, performance, and reliability. By carefully considering factors like material, design, and operating environment, you can create a spring that perfectly suits your needs. Partnering with a trusted manufacturer LIKE LINSPRING ensures a seamless process from design to production, helping you achieve optimal results.
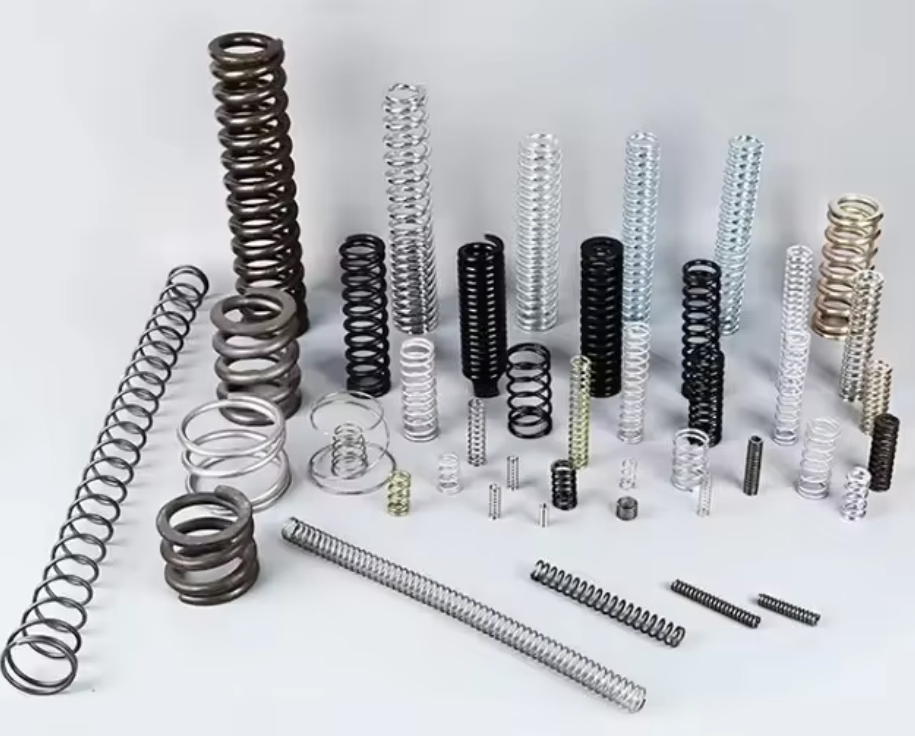
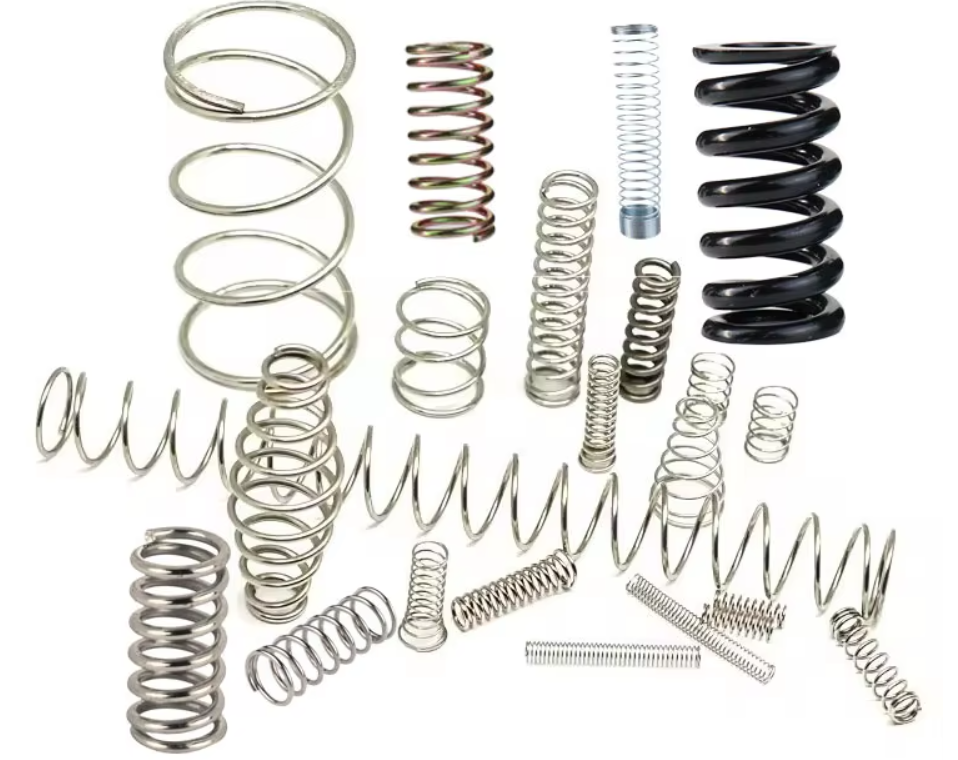


Still unsure which material fits your needs? Let’s discuss your specific application. Whether it’s automotive, aerospace, or precision engineering, we can help you select the perfect material tailored to your requirements.
Would you like a tailored recommendation or a deeper dive into one of the materials? Let’s make your project a success!
Email: sales@linspring.net
Phone:+86-13599531763
Address: Unit 502, floor 5, Building B, # 1 workshop, Auto Industry City Parts Supporting Center (phase iv), Guankou Town, Jimei District, Xiamen,Fujian,China
We will contact you within 1 working day.