




Our springs are crafted to meet exact specifications, ensuring superior performance and reliability.

From stainless steel to specialized alloys, we work with a variety of materials to meet your requirements.

Whether you need compression springs, torsion akasupe, extension springs, or wire forms, we deliver custom solutions.

Direct factory pricing ensures you get the best value for top-tier quality.

Streamlined processes allow us to deliver your orders on time, every time.

We efficiently handle international logistics to deliver anywhere in the world.
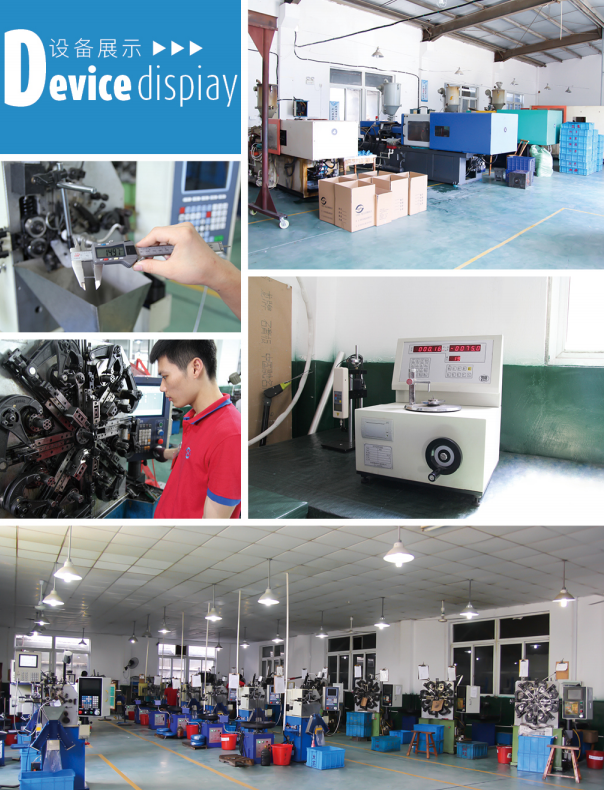
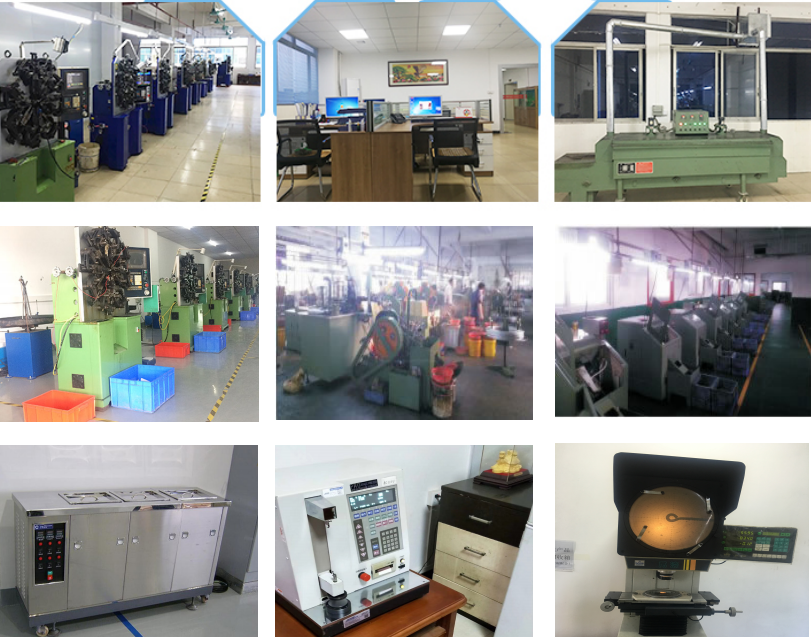



Springs are the unsung heroes in many industries, providing the flexibility, mphamvu, and precision needed for countless applications. Whether you’re designing high-performance machinery or everyday tools, selecting the right material ensures reliability, kukhazikika, and cost-effectiveness. Let’s break down the essentials to help you make an informed decision!
Spring steels are incredibly popular due to their combination of elasticity, tensile strength, and fatigue resistance. They’re ideal for applications where springs are under constant stress or load.
Ngati ntchito yanu imakhudzana ndi chinyezi, mankhala, kapena nyengo yoipa, chitsulo chosapanga dzimbiri ndi gawo lanu. Izi zikugwirizana ndi dzimbiri ndikuonetsetsa kuti ndi nthawi yayitali.
Nthawi zina, your application calls for something extra. That’s where specialty materials like superalloys and high-strength composites come in.
Case 1: Marine Equipment Manufacturer
A client designing springs for deep-sea applications chose 316L stainless steel for its superior resistance to saltwater corrosion. This decision doubled the service life of their products and reduced maintenance costs by 30%.
Case 2: Heavy Machinery Builder
A manufacturer of industrial presses switched to SWP alloy steel for their tension springs. The result? Springs withstood 20% higher loads and lasted 50% longer under continuous operation.
Case 3: Food Processing Startup
For springs in food slicers, 304 chitsulo chosapanga dzimbiri was the perfect choice due to its affordability and compliance with food safety standards. Kuyambira kupulumutsidwa 15% pa mtengo pomwe akuwonetsetsa hggienic.
| Serial ayi. | Kalasi yachitsulo | C (%) | Ndi (%) | Mn (%) | Mowa (%) | MO (%) | V (%) | B (%) | Mu (%) | C (%) | Tsa (%) | M (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 65 | 0.62-0.70 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤ 0.25 | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 2 | 70 | 0.62-0.75 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤ 0.25 | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 3 | 85 | 0.72-0.85 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤ 0.25 | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 4 | 65Mn | 0.62-0.70 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.90-1.20 | ≤ 0.25 | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 5 | 55Si2mn | 0.52-0.60 | 1.50-2.00 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤ 0.35 | - | - | - | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 6 | 55To2mnb | 0.52-0.60 | 1.50-2.00 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤ 0.35 | - | - | 0.0005-0.004 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 7 | 55Si2mn etc. | 0.52-0.60 | 0.70-1.00 | 1.00-1.30 | ≤ 0.35 | - | 0.08-0.16 | 0.0005-0.0035 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 8 | 60Si2mn | 0.56-0.64 | 1.50-2.00 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤ 0.35 | - | - | - | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 9 | 60Si2mna | 0.56-0.64 | 1.60-2.00 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤ 0.35 | - | - | - | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.030 |
| 10 | 60Si2cra | 0.56-0.64 | 1.40-1.80 | 0.40-0.70 | 0.70-1.00 | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.030 |
| 11 | 55Nyongolotsi | 0.56-0.64 | 1.40-1.80 | 0.40-0.70 | 0.90-1.20 | - | 0.10-0.20 | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 12 | 60Crimna | 0.56-0.64 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.70-1.00 | 0.70-1.00 | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 13 | 50Nyongolotsi | 0.46-0.54 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.50-0.80 | 0.80-1.10 | - | 0.10-0.20 | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| 14 | 30CVV2A | 0.26-0.34 | 0.17-0.37 | ≤ 0.40 | 2.00-2.50 | - | 0.50-0.80 | 4.4-5.0 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
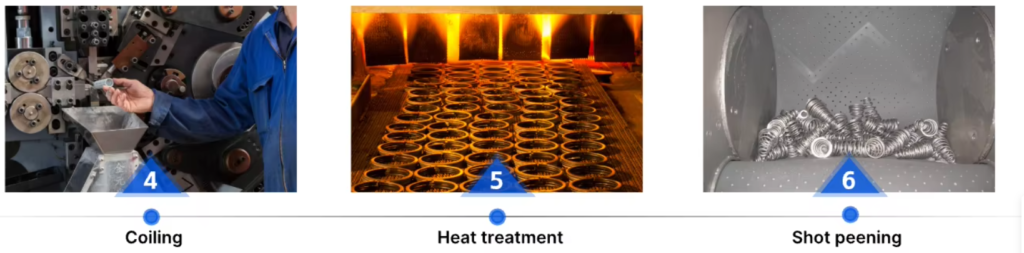
Spring heat treatment is essential for optimizing mechanical properties, ensuring durability, and enhancing fatigue resistance. Various strengthening techniques, such as quenching, tempering, and surface treatments, are applied based on material type and application requirements.
The heat treatment process for springs can be categorized into three types:
The quenching process ensures uniform martensitic transformation, followed by tempering to relieve stress and enhance toughness. Techniques such as isothermal tempering further improve plasticity and toughness, ensuring the spring maintains dimensional accuracy and mechanical stability.
| Process Type | Kufotokozera | Materials Used | Key Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching & Tempering | Heating above Ac3, holding, then rapid cooling and tempering. | High-carbon steel, alloy steel | Increases strength, hardness, and elasticity. |
| Cold Work Strengthening | Uses mechanical deformation instead of heat treatment. | Stainless steel wire, cold-rolled steel strips | Enhances work-hardening properties. |
| Aging Treatment | Additional heat stabilization after initial processing. | Certain alloy materials | Improves stability and strength. |
| Isothermal Quenching | Maintains temperature above Ms, cools in molten salt. | High-carbon steel, alloy springs | Enhances toughness and plasticity. |
| Controlled Tempering | Gradual cooling to prevent deformation. | Precision springs, mechanical components | Reduces internal stress and ensures accuracy. |
This structured approach ensures that each heat treatment method is aligned with specific material properties and application requirements for optimized performance.
The heat treatment of springs:
| Njira | Process Description | Key Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Heat Treatment | Heating and cooling steel to adjust mechanical properties | Increases strength, elasticity, and durability | Medium to high-carbon steel springs |
| Surface Hardening Treatment | Carburizing, nitriding, or induction hardening of the outer layer | Enhances wear resistance while keeping core toughness | Automotive and industrial springs |
| Aging & Tempering | Heat treatment to relieve internal stresses and refine microstructure | Improves stability and mechanical consistency | Precision and high-load springs |
| Kalasi yachitsulo | Austenitizing Temperature (°C) | Isothermal Quenching Temperature (°C) | Cooling Time (min) | Hardness (HRC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | 820 ± 10 | 320 – 340 | 15 – 20 | 46 – 48 |
| 60Si2mna | 870 ± 10 | 260 | 20 – 25 | 50 – 52 |
| 50Nyongolotsi | 850 ± 10 | 300 | 20 – 25 | 55 – 57 |
| Steel Type | Heat Treatment Process | Hardness (HRC) | Kulimba kwamakokedwe (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Impact Toughness (J/cm²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50Nyongolotsi | Conventional Quenching + Tempering | 48 | 1750 | 1500 | 10 | 44 |
| 60Si2mna | Isothermal Quenching + Tempering | 47 | 1900 | 1750 | 11 | 46 |
| 65Si2MnWA | Isothermal Quenching + Tempering | 50 | 2100 | 1980 | 9 | 43 |
This table format provides a clear and organized comparison of different heat treatment techniques for springs.

Xiamen Linspring was able to manufacture my custom order to specifications and was helpful and communicatie along the way.The quality of the delivered product was good.

This was my second order with Linspring. The seller is great to communicate with and the spring were perfect,just like the first order. Thank you for your prompt,courteous.

Wokondwa kwambiri ndi akasupe athu. Pa nthawi ndi kutumiza kunali kwachangu
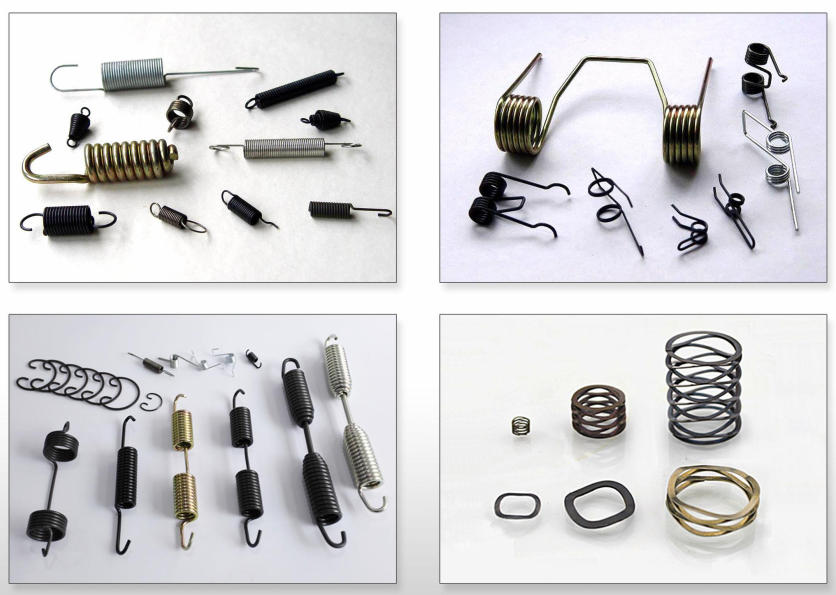



Akasupe ndizofunikira pazolinga zosawerengeka, Kuchokera ku matontho apamadzi ndi aerospace toza matenda azachipatala ndi zida zapanyumba. Akasupe, makamaka, Patsani mayankho ogwirizana kuti mukwaniritse zofunika kuchita, kukula, malaya, ndi ntchito. Kupanga chizolowezi cha chizolowezi kumafuna kuganizira zambiri, Kuchokera pakugwira ntchito kwa nyengo.
Kuphatikizika kwa Springs
Tension Springs
Springs Springs
Flat Springs
Specialty Springs
Choosing the right material is critical for the performance and durability of a custom spring. Some common materials include:
Chitsulo cha Carbon
Chitsulo chosapanga dzimbiri
Alloy Steel
Phosphor Bronze and Beryllium Copper
Titaniyamu
Inconel and Other Superalloys
When designing a custom spring, there are several factors to consider:
Mtundu Wamsika: Choose the appropriate spring type (kukanikiza, kukangana, ndi zina.) based on the application.
Zofunikira:
Spring Dimensions:
Kusankha Zinthu: Choose a material that meets the application’s environmental, mphamvu, and durability requirements.
Stress and Fatigue:
Malo Ogwirira Ntchito:
Mtundu Womaliza:
Manufacturing Constraints:
Tanthauzirani Zofunikira Zanu:
Choose a Material:
Work with LINSPRING:
Prototype Development:
Final Production:
Provide Clear Specifications:
Pemphani Zitsanzo:
Fotokozerani kutsatira:
Katswiri Wopeza:
Konzekerani Kupumula:
Springs Springs ndi masewera osewerera pazomwe zimafuna kulondola, chionetsero, ndi kudalirika. Mwa kulingalira bwino zinthu monga zakuthupi, jambula, ndi malo ogwiritsira ntchito, Mutha kupanga kasupe yemwe amakwaniritsa zosowa zanu. Omwe Akufuna Kuchita Ndi Woumba Wosakhulupirira Monga Linga Linmiretion Amatsimikizira Njira Zopanda Zosanjikiza Kuchokera Kupanga, kukuthandizani kuti mukwaniritse zotsatira zabwino.
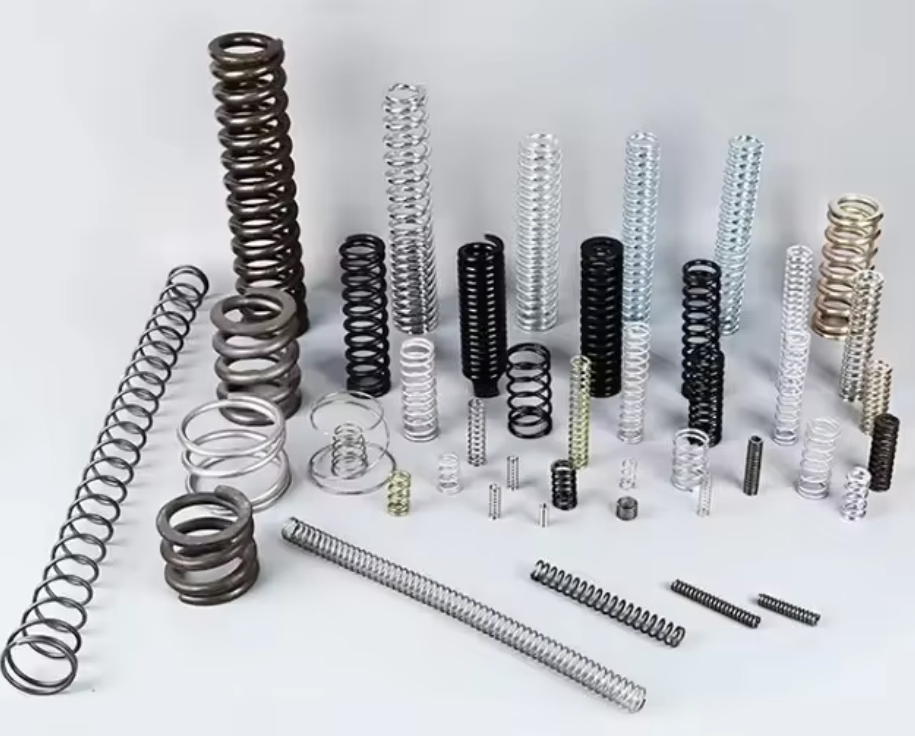


Osatsimikiza kuti ndi zofunika ziti zomwe zikugwirizana ndi zosowa zanu? Tiyeni tikambirane pulogalamu yanu. Kaya ndi magetsi, amongoce, kapena upangiri woyenera, Titha kukuthandizani kusankha zinthu zabwino zogwirizana ndi zomwe mukufuna.
Kodi mungafune kuvomerezedwa kapena kulowa mkati mwamiyala imodzi? Tiyeni tichite bwino!
Imelo: Tulutsani@linpring.net
Foni:+86-13599531763
Adilesi: Chigawo 502, pansi 5, Nyumba B, # 1 msonkhano, Auto Industry City Parts Support Center (gawo iv), Mzinda wa Guankou, Chigawo cha Jimei, Xiameni,Fujian,China
Tidzakulumikizani mkati 1 tsiku la ntchito.